cirrhosis
understand cirrhosis, its consequences and possible treatments
Cirrhosis
a silent disease
While the liver is an organ capable of regenerating itself, it can also retain scars in the event of chronic aggression and form fibrosis. This "fibrosis" or scar tissue associated with regeneration nodules that draw a bumpy outline on the organ, alter its function and lead after a few years to the occurrence of cirrhosis.
In France, there are between 1,500 and 2,500 cases of cirrhosis per million inhabitants, with approximately 150 to 200 cases discovered per million inhabitants each year. Cirrhosis and its complications are responsible for approximately 15,000 deaths each year among relatively young patients (average age 55).
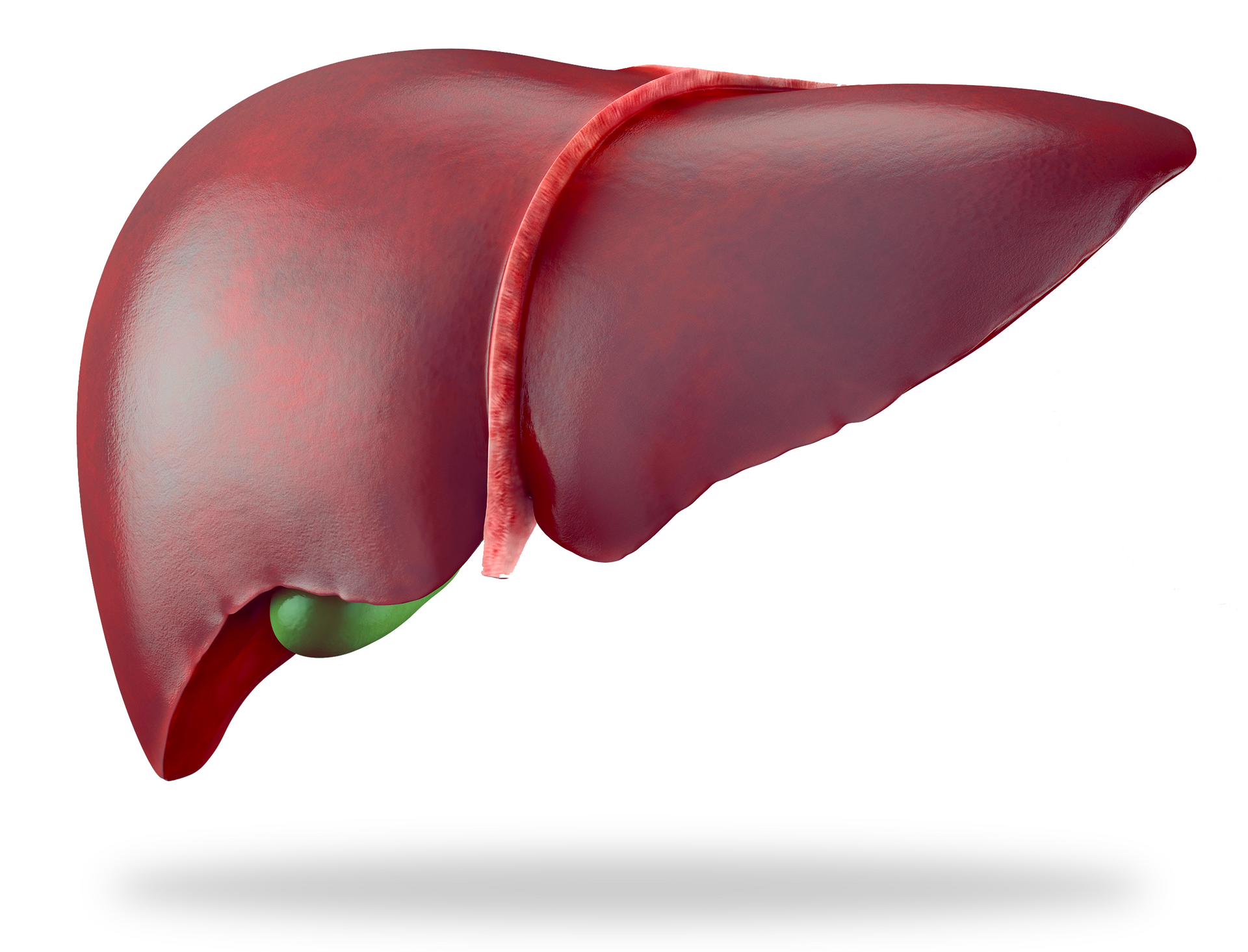
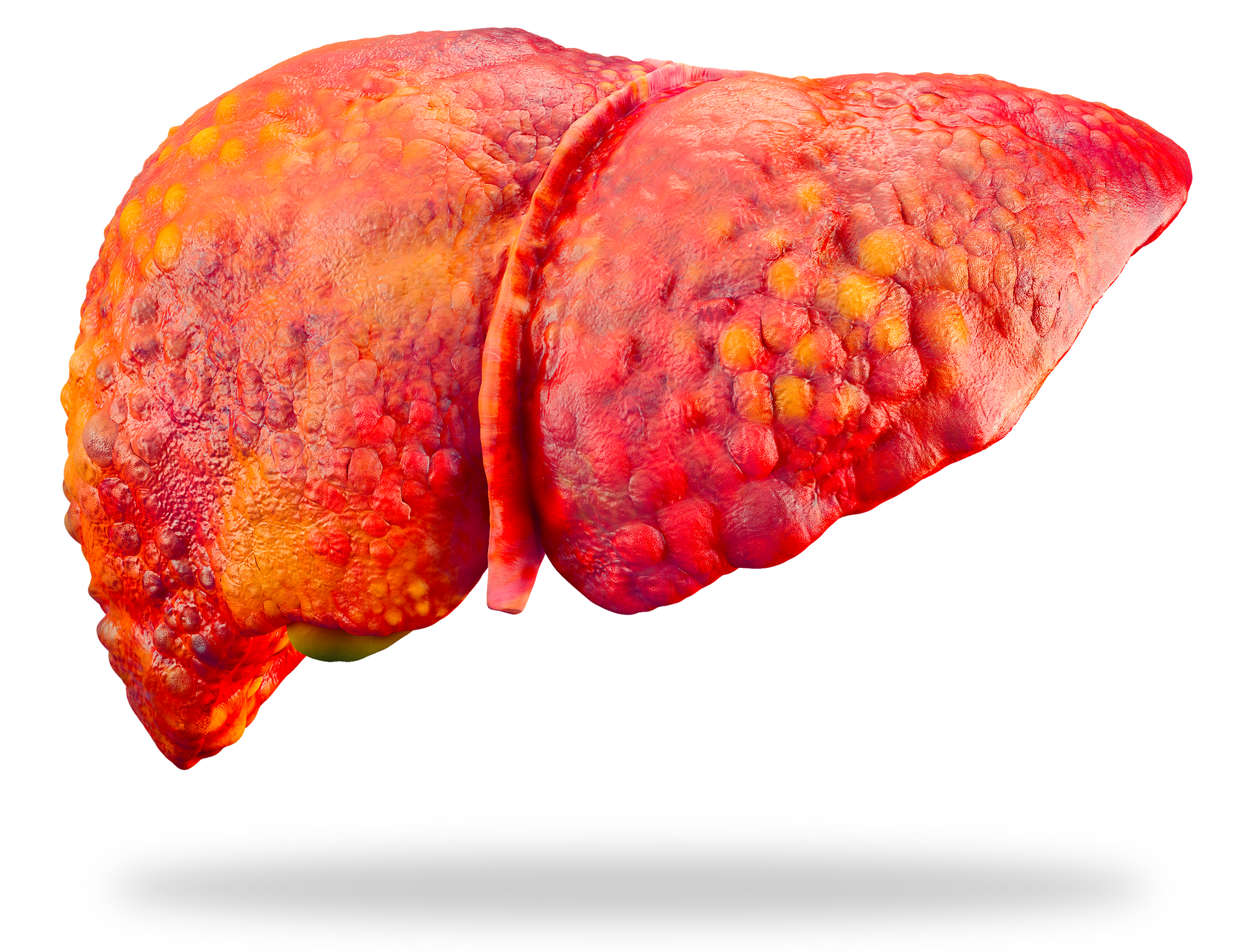
Move the cursor left or right
-
The different causes of cirrhosis
- Alone or in combination, several aggressive agents can cause cirrhosis such as:
- Regular alcohol consumption (> 2 glasses/day in women, > 3 glasses/day in men) is a common cause in France, c
- Certain chronic viral hepatitis (hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D)
- Overweight and metabolic syndrome with an accumulation of fat in the liver responsible for chronic inflammation, are also an increasingly frequently mentioned cause
- Many chronic liver diseases can also be involved: autoimmune diseases, genetic diseases (hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, etc.), biliary tract diseases, etc.,
Liver decompensation
-
Ascites
Ascites is a common condition in people with cirrhosis. It is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, which can lead to swelling and discomfort. The primary goal of ascites treatment is to reduce the amount of fluid in the abdomen. This can be achieved with medications called diuretics, such as furosemide and spironolactone, which help remove excess fluid through the kidneys. Doses may be adjusted based on your response and tolerance to treatment, including regular blood tests to assess your kidney function and electrolyte levels. In addition to diuretics, it is important to adjust your diet. Reducing salt intake can help decrease fluid retention in the body. It is also important to avoid alcohol, as this can worsen cirrhosis and ascites. In some cases, when ascites is severe or does not respond to the treatments mentioned above, an ascites puncture may be necessary. This is a medical procedure in which abdominal fluid is removed using a needle and catheter, allowing for rapid symptom relief and fluid analysis. In cases where ascites does not respond to conventional treatments or if it recurs frequently, your doctor may consider a treatment option called TIPS. TIPS aims to reduce pressure in the liver's blood vessels and relieve fluid buildup in the abdomen. However, this procedure carries risks and requires a thorough assessment of your health before being considered. If the previous procedures fail, a liver transplant may also be considered to control ascites. This procedure aims to replace a failing liver with a healthy one and restore normal liver function.
-
Hepatic encephalopathy
- Hepatic encephalopathy refers to all neurological disorders secondary to advanced liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, in the absence of another obvious neurological cause. It can manifest as simple slowing down or confusion, and can be responsible for drowsiness, even coma. It is caused by the accumulation of certain toxins (including ammonium) in the brain due to liver dysfunction since one of the main roles of the liver is to eliminate toxins, particularly those from the digestive tract. The treatment of hepatic encephalopathy is based on the treatment of the triggering factor and specific treatment. Medications can be prescribed to help reduce the symptoms of encephalopathy.
- Lactulose, the first-line treatment, causes the acceleration of transit and a reduction in bacterial proliferation, limiting the passage of toxins from the intestine to the liver. To prevent recurrence, rifaximin (a specific digestive tract antibiotic) can also be used to reduce the amount of toxins in the body and improve cognitive function. It is also important to avoid toxic substances such as alcohol consumption and the use of medications such as sedatives, which can worsen hepatic encephalopathy and promote flare-ups. If hepatic encephalopathy does not respond to conventional treatments or recurs frequently, a liver transplant may be considered.
In the absence of early medical treatment, cirrhosis progresses to decompensation (stage where the liver is no longer able to fully perform its functions), and symptoms linked to complications appear such as:
- Jaundice (icterus), swelling of the lower limbs,
- Blood in the stool or during vomiting linked to the presence of esophageal varices
- Infections
or other more important ones:
Patient pathways
for patients with liver cirrhosis
When it comes to liver disease and its treatment, the patient pathway is of great importance. It will allow you, as a patient, to personalize your care pathway, from assessment to RCP, from hospitalization to consultations with internal or external specialists, the patient pathway allows you to better manage all phases of the disease.
CIRRHOSIS EXPRESS
Every Friday, we can receive a patient with discovery of cirrhosis and/or liver tumor.
violaine.gautier@aphp.fr
0142161034.